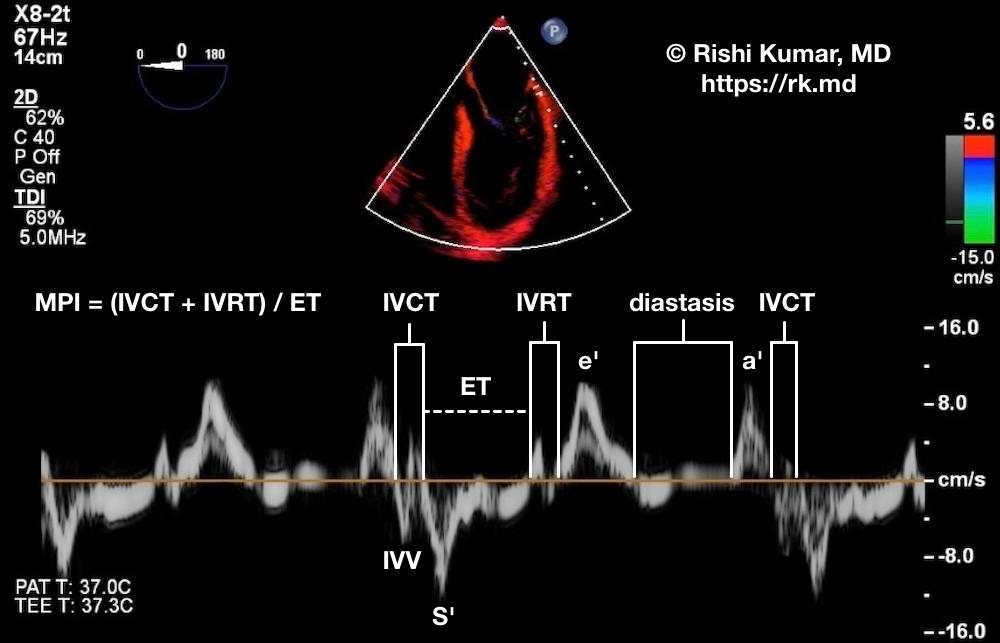
As part of a comprehensive left ventricular (LV) diastolic assessment, doppler tissue imaging (DTI) of the medial and lateral aspects of the mitral valve (MV) annulus should be performed. In the image below, I have labeled a DTI of the lateral aspect of the MV derived from a mid-esophageal 4-chamber TEE view.
Systole includes isovolumetric contraction time (IVCT) and ejection time (ET). The Doppler profile’s systolic component (S’) correlates with LV ejection fraction and should be > 8 cm/s.
Diastole includes isovolumetric relaxation time (IVRT) representing the time from aortic valve closure till the MV opens, early rapid filling tissue velocity (e’), diastasis, and late diastolic atrial contraction tissue velocity (a’).
The myocardial performance index (MPI), otherwise known as the Tei index, is a global measure of ventricular systolic/diastolic function that is less dependent on loading and geometric conditions. Mathematically, MPI = (IVCT + IVRT) / ET. Because ET represents the time blood is being ejected, a higher ET (lower MPI) is better. Normal MPIs for the LV and RV are 0.39 ± 0.05 and 0.28 + 0.04, respectively.