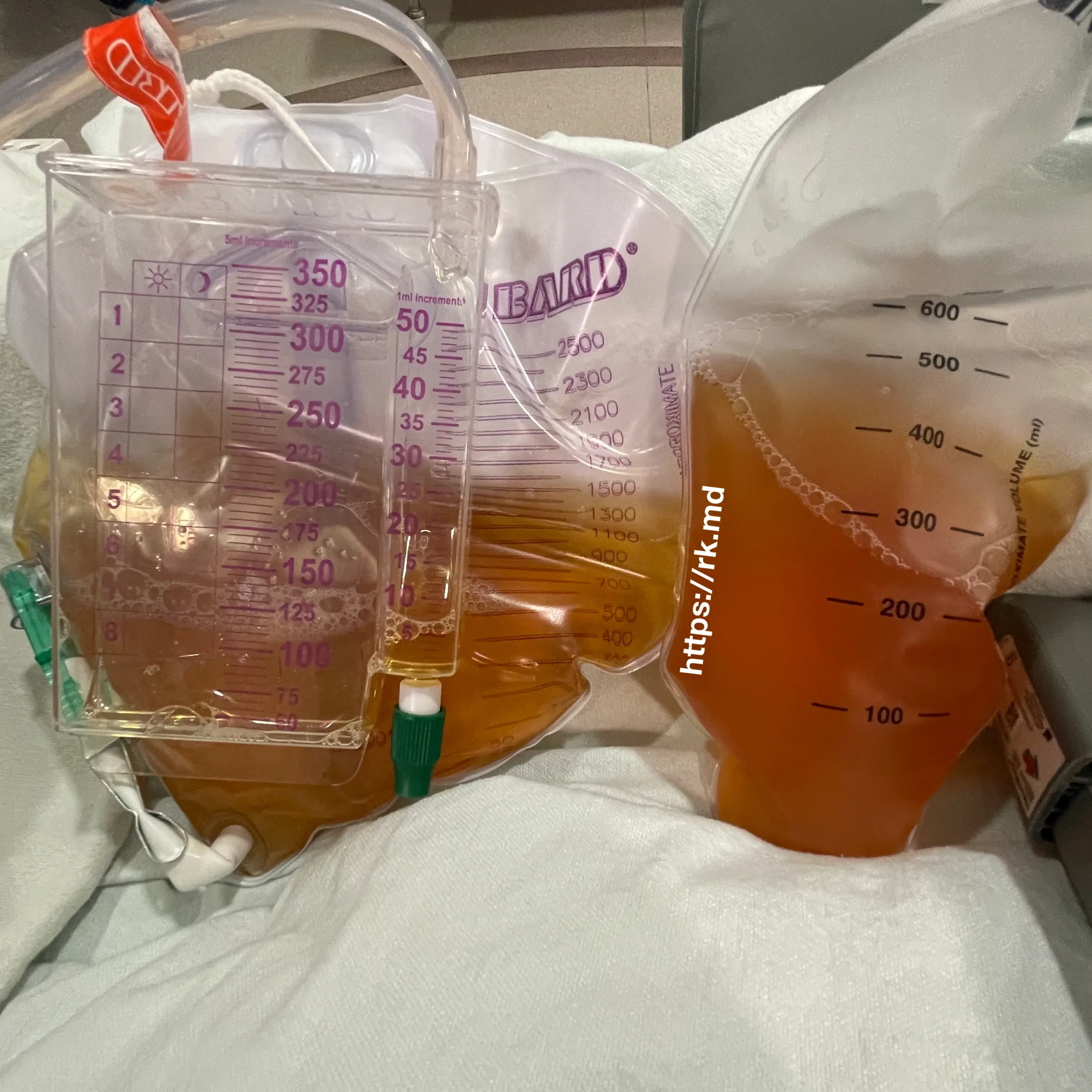
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear and colorless fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord, providing cushioning and nutrients to the central nervous system. Xanthochromia (Greek for “yellow color”) refers to the yellow discoloration of the CSF, which can indicate the presence of blood breakdown products such as bilirubin or hemoglobin.
Xanthochromia in the CSF can suggest conditions ranging from subarachnoid hemorrhage and traumatic brain injury to certain infections and tumors. Bleeding in the central nervous system can also irritate the meninges – the thin layers of tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord – causing headaches, nuchal rigidity, confusion, etc.
The pictured image shows collected CSF (right) next to urine from a Foley catheter (left). Just as CSF xanthochromia is a result of breaking down blood, urine gets its yellow color from urobilin – a waste product of degrading heme (precursor of hemoglobin).