A left ventricular (LV) pseudoaneurysm is an LV outpouching devoid of myocardium/endocardium contained by the pericardium and adhesions. As one can imagine, this pathology carries a high risk of rupture and mortality. LV pseudoaneurysms are most commonly linked to myocardial infarction (inferior > anterior) but can also follow open-heart surgery (e.g., mitral valve procedures).
Symptoms are nonspecific and span from mild chest pain with shortness of breath to congestive heart failure and even sudden cardiac death. Keep in mind many patients are completely asymptomatic! Early diagnosis is centered around angiography which typically reveals a “narrow neck” pseudoaneurysm connected to the LV. Other diagnostic modalities include echocardiography, ventriculography, and cardiac CT/MRI.
Operative intervention is the mainstay therapeutic option. Timing this procedure is important, and often times mechanical circulatory support devices like TandemHeart are used to unload the left heart allowing it to rest.
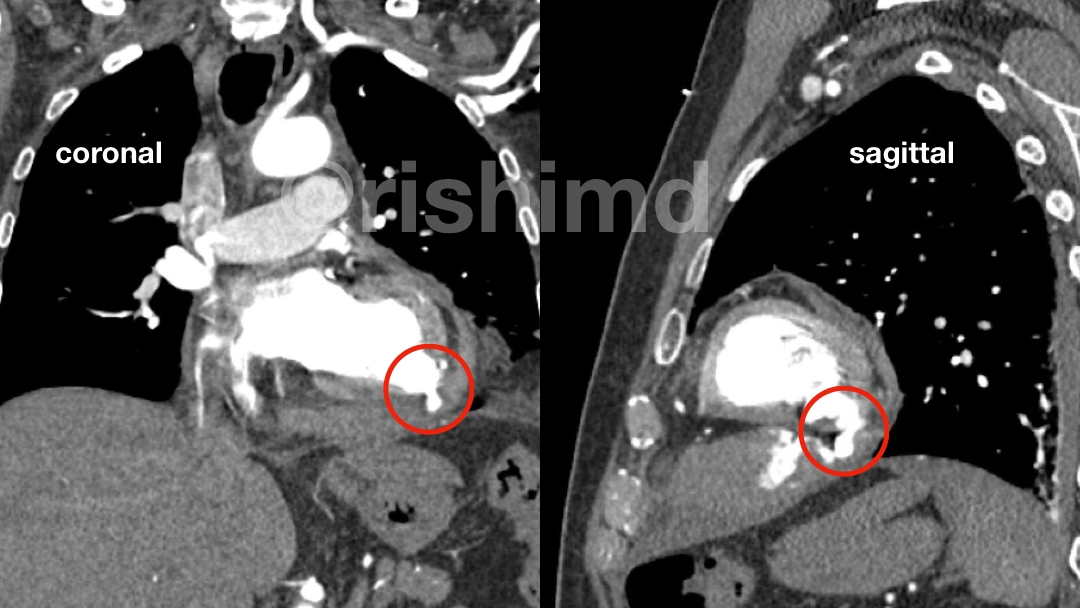
The pictured coronal (in front of) and sagittal (from the side) slices of the CT angiogram highlight a left ventricular pseudoaneurysm perforating into the pericardium (encircled in red) resulting in hemopericardium with mass effect on the right heart. The ventriculogram shows active extravasation of contrast through the inferior LV. Needless to say, at this point, medical management is less of an option and emergent surgical intervention is warranted.





